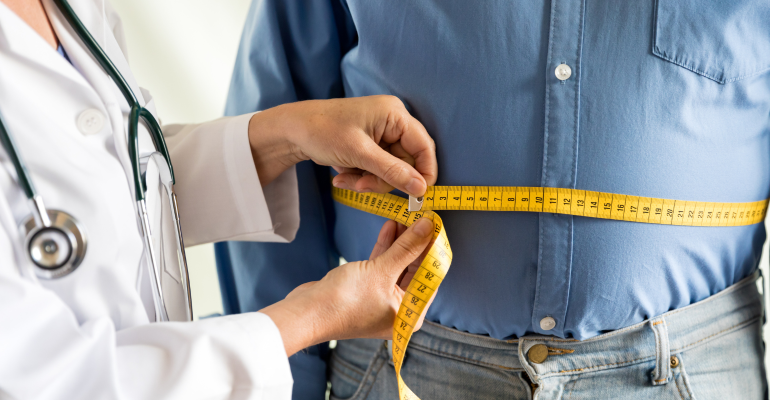
According to the World Health Organization, worldwide obesity has nearly tripled since 1975, while in 2016, more than 1.9 billion adults were overweight, and over 650 million were obese. World Obesity Day marks an occasion to revisit the urgency of tackling this urgency and the need to create awareness of the issue. We explore what obesity is, how to measure it, and its social and health ramifications.
Obesity is defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that may impair health. It is usually an outcome of an energy imbalance between calories consumed and spent by an individual.
How to measure obesity?
Body mass index (BMI) is an indicator of obesity. It is a simple index of weight-for-height that can be calculated and used to classify overweight and obesity in adults. It is defined as a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of his height in meters (kg/m2). A BMI greater than or equal to 25 qualifies as obesity.
What is the impact of obesity on society?
Obesity as a social stigma
Socially, obesity is commonly stigmatized. People who are obese are often subject to discrimination and prejudice. This often leads to social isolation, lower self-esteem, and depression among obese individuals. As a society, it is crucial to raise awareness that obesity is a disease and not a personal failure. Therefore, it’s essential to support people in their efforts to manage and prevent obesity.
Obesity as a health concern
While being overweight may seem like a cosmetic concern on the surface, it also has several health ramifications beyond. Obesity often leads to comorbidities like diabetes and heart disease. Statistics from the WHO reveals that obesity is one of the leading causes of preventable death worldwide. In fact, most of the world’s population lives in countries where overweight and obesity kills more people than underweight.
Surprisingly, childhood obesity is also a major concern. Around 39 million children under the age of five were overweight or obese in 2020. It has been seen that childhood obesity leads to several health issues, such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and asthma, from a tender age. Therefore, it is crucial to promote healthy eating habits and physical activity from an early age to prevent childhood obesity.
How is the Middle East attempting to tackle obesity?
Obesity is a significant concern in the Gulf region, and governments are proactively taking measures to reverse the trend. Data suggests that about 70 per cent of Saudis, especially children and youth, who account for at least 50 per cent of the population, are obese or overweight.
In that vein, the Saudi government is taking proactive steps to tackle the obesity epidemic. The Saudi national strategy for diet and physical activity up to 2025 targets:
- Lowering the rate of overweight and obesity to 40 per cent.
- Lowering the rate of people with low physical activity to 20 per cent.
- Increasing vegetable and fruit consumption (5 units/day) from 8.4 per cent to 20 per cent among males and from 4.5 per cent to 20 per cent among females.
- To stabilize the prevalence rate of hyperlipidemia at 19.3 per cent.
- To stabilize the prevalence rate of diabetes mellitus at 18 per cent.
The UAE is also taking measures. The country launched the National Program for Happiness and Wellbeing, which aims to promote healthy living and reduce nutrition-related lifestyle diseases, including diabetes and obesity.
With growing awareness, and governments, individuals, and the health sector working together towards defeating this epidemic, we can expect a reversal in suboptimal lifestyle trends and a healthier obesity-free world in the years to come.